
 nootro
nootro

 2017-10-31
2017-10-31
 0
0
 4918
4918
Aging is becoming an international challenge to healthcare systems in both developed and developing countries. Small molecules capable of improving the health of older individuals are being explored. Small molecules that enhance cellular stress resistance are a promising avenue to alleviate declines seen in human aging.
A paper ,written by Evandro F. Fang, which published in Nature showed that tomatidine, a natural ingredient exist in tomato ,extends lifespan and healthspan in C. elegans .And C. elegans is an animal model of aging which shares many major longevity pathways with mammals.
In their experiment, they found that:
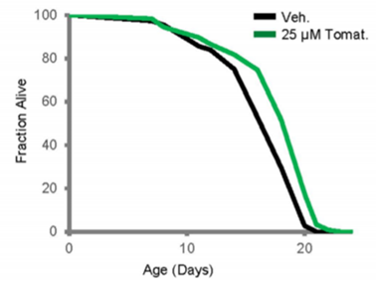
1. Tomatidine extends lifespan of wild-type C. elegans. L
Researchers exposed N2 (wild type) C. elegans to tomatidine at concentrations of 0,25 and 50μM beginning at the L4 stage. Tomatidine consistently extended lifespan at a concentration of 25μM with (7.0± 0.8)% increase, while there was no significant change of lifespan at 50μM. When assessing the survival curve further, it was noted that many C. elegans exposed to 50 μM tomatidine died at relatively early ages (7 to 13 days) compared to C. elegans not exposed to tomatidine, but those that survived this period of increased death had a longer maximal lifespan.
2. Tomatidine enhances muscle function and modulates metabolism in C. elegans
There is a dramatic physical decline in swimming ability, pharyngeal pumping, and maximum movement velocity as C. elegans age. C. elegans treated with 25 μM tomatidine exhibited enhanced pharyngeal pumping at multiple time points during their life. Although 25 μM tomatidine did not affect swimming ability in young (adult day 4) C. elegans, as they aged (adult day 12), tomatidine significantly delayed the age-related decrease of swimming movement scores (48% improvement compared with vehicle).They verified the decrease of maximum movement velocity with age in N2 C. elegans, but found no significant differences in maximum movement velocity in tomatidine-treated C. elegans from adult days 4 to 10 compared with vehicle treatment. Collectively, tomatidine is able to alleviate some features of aging-related physical decline in C. elegans, which indicates an improvement in healthspan.And the improvement of swimming and pharyngeal pumping implied inhibition of sarcopenia.
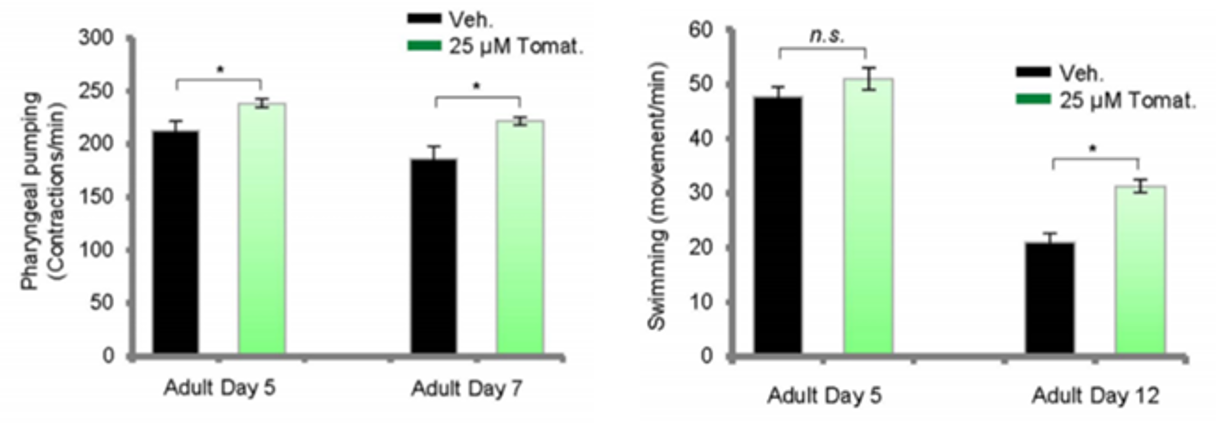
3. Tomatidine affects mitochondrial function and ROS metabolism
They next investigated the mechanism(s) by which tomatidine enhances lifespan and muscle-related healthspan. To this end, we performed whole-genome gene expression analysis using microarrays to elucidate potential pathways that might mediate the anti-aging action of tomatidine.
Those data suggest that tomatidine affects mitochondrial function and ROS metabolism.
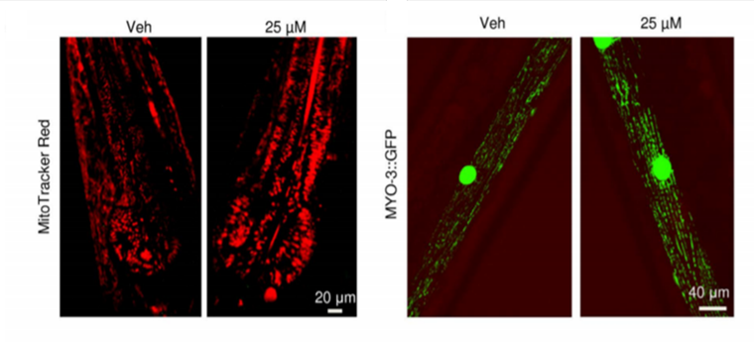
4. Tomatidine affects mitochondrial content and quality.
The pharynx is an important organ composed of pharyngeal muscles that show age-dependent loss of function and structure, which are attenuated by tomatidine. We therefore examined mitochondrial distribution in the pharynx using MitoTracker Red. There were more mitochondria in pharyngeal cells in tomatidine-treated C. elegans compared with vehicle control .
5. Tomatidine induces mitophagy by activating the SKN-1/Nrf2 pathway.
To elucidate the signaling pathway(s) by which tomatidine stimulates mitophagy, they used fluorescent reporter techniques and human HEK- 293 cells to determine whether tomatidine affected the promoter activity of several transcriptional activators that regulate mitochondrial homeostasis. These include the longevity and autophagy-regulating protein SIRT1, the master regulator of mitochondrial biogenesis PGC-1α, and the anti-oxidant nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2)/antioxidant response element (ARE) pathway. While tomatidine did not affect SIRT1 or PGC-1α promotor activities (Figure S3A,B), tomatidine induced a significant increase of Nrf2/ARE reporter activity in a concentration-dependent manner.
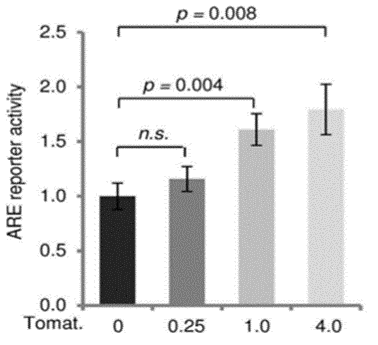
Compromised mitochondrial quality and function contributes to biological and pathological aging, and many major aging-related diseases. Accumulation of damaged mitochondria within cells can trigger apoptosis, inflammation, and cell senescence.
The group of Evandro F. Fang found that tomatidine preserves muscle function during aging, and extends lifespan, in C. elegans. Further studies are necessary to dissect the specificity of the beneficial effects of tomatidine in C. elegans. For example, it is conceivable that the bacteria upon which the worms feed could metabolize tomatidine to a different compound that, in turn, exerts a beneficial effect on the worms. However, it is important to note that tomatidine improves mitophagy in both C. elegans and cultured human cells that lack bacteria. Additionally, it would be interesting to investigate whether other steroids with a similar structure to tomatidine produce similar effects in C. elegans.
Reference
[1]Son, T. G. et al. Naphthazarin protects against glutamate-induced neuronal death via activation of the Nrf2/ARE pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 433, 602–606 (2013).
[2]Johnson, J. A. et al. The Nrf2-ARE pathway: an indicator and modulator of oxidative stress in neurodegeneration. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 1147, 61–69 (2008).
[3]Dinkova-Kostova, A. T. & Abramov, A. Y. The emerging role of Nrf2 in mitochondrial function. Free Radic Biol Med 88, 179–188 (2015).
[4]Nargund, A. M., Pellegrino, M. W., Fiorese, C. J., Baker, B. M. & Haynes, C. M. Mitochondrial Import Efficiency of ATFS-1 Regulates Mitochondrial UPR Activation. Science 337, 587–590 (2012).
[5]Fang, E. F. et al. A research agenda for aging in China in the 21st century. Ageing research reviews (2015).
[6]Longo, V. D. et al. Interventions to Slow Aging in Humans: Are We Ready? Aging cell (2015).
[7] Fang E F, Waltz T B, Kassahun H, et al. Tomatidine enhances lifespan and healthspan in C. elegans through mitophagy induction via the SKN-1/Nrf2 pathway[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7:46208.
Diabetes, often referred to by doctors as diabetes mellitus, des... More

 0
0

 0
0
According to research, myricetin stimulates glucose transport in... More

 0
0

 1
1
In vivo, betaine acts as a methyl donor for the conversion of h... More

 0
0

 0
0
There are many studies at the molecular, biochemical, organism a... More

 0
0

 0
0
Apigenin, an abundant dietary flavonoid, is emerging as a potent... More

 0
0

 0
0
BVC synergised with thiazolidinediones, which are synthetic PPAR... More

 0
0

 0
0
Epicatechin is an antioxidant flavonoid, occurring especially in... More

 6
6

 2
2
Fatigue is a very common phenomenon. There are many reasons can ... More

 2
2

 1
1
There are some simple steps can be taken to prevent or slow bone... More

 0
0

 0
0
Echinacea is also called the magic herb that can bring health to... More

 0
0

 0
0
Obesity has become a global health issue. It is a medical condit... More

 0
0

 0
0
Cardiac hypertrophy is the myocardial response to various pathol... More

 7
7

 1
1
Aging is becoming an international challenge to healthcare syste... More

 0
0

 0
0
Asthma is a common long-term inflammatory disease of the airways... More

 0
0

 0
0
Studies have shown that this compound possesses a plethora of b... More

 0
0

 0
0
